GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMADABAD, GUJARAT
DIPLOMA ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
COURSE TITLE: ELECTRIC TRACTION AND CONTROL
(Course Code: 3350907)
5th Semester
UNIT – 1 Traction Systems and Latest Trends
1.1 Present scenario of Indian Railways – High speed traction, Metro
1.2 Latest trends in traction-Metro, monorail, Magnetic levitation Vehicle
1.3 Steam, diesel, diesel-electric, Battery and electric traction systems
1.4 General arrangement of D.C.,A.C. single phase, 3 phase,Composite systems
1.5 Choice of traction system – Diesel- Electric or Electric
UNIT– 2 Mechanics of Train Movement
2.1 Analysis of speed time curves for main line, suburban and urban services
2.2 Simplified speed time curves.
2.3 Relationship between principal quantities in speed time curves
2.4 Requirement of tractive effort
2.5 Specific energy consumption and Factors affecting it.
UNIT– 3 Traction Motors and Their Control
3.1 Features of traction motors.
3.2 Significance of D.C. series motor as traction motor
3.3 A. C. Traction motors-single phase, Three phase, Linear Induction Motor
3.4 Comparison between different traction motors
3.5 Series-parallel control
3.6 Open circuit, Shunt and bridge transition
3.7 Pulse Width Modulation control of induction motors
3.8 Types of electric braking system.
UNIT- 4 Electric Locomotives and Auxiliary Equipment
4.1 Important features of electric locomotives
4.2 Different types of locomotives
4.3 Current collecting equipment
4.4 Coach wiring and lighting devices
4.5 Power conversion and transmission systems
4.6 Control and auxiliary equipment.
UNIT- 5 Feeding and Distribution System.
5.1 Distribution systems pertaining to traction (distributions and feeders)
5.2 Traction sub-station requirements and selection
5.3 Method of feeding the traction sub- station
For official syllabus go to: https://www.gtu.ac.in/
The country is leading towards the railway electrification and also moving towards metro, monorail system. The diploma student is required to know about the electric traction scheme and its latest trends. This subject is offered as one of the elective, highlighting the current and future trends in traction systems, auxiliary equipment, electric locomotives, control of traction motors and future-trends. The Diploma pass student with this elective will be able to maintain the traction systems, auxiliary equipment, electric locomotives and traction motors.
The course content should be taught and implemented with the aim to develop different types of skills so that students are able to acquire following competency:
- Maintain traction systems, auxiliary equipment, electric locomotives and traction motors.
The theory should be taught and practical should be undertaken in such a manner that students are able to acquire different learning outcomes in cognitive, psychomotor and affective domains to demonstrate the following course outcomes:
i. Distinguish different traction systems and latest trends in traction systems.
ii. Differentiate services of traction system based on speed time curve.
iii. Control different types of traction motors
iv. Use various traction system auxiliaries.
v. Explain the distribution system of a traction system.
i. www.irieen.com (Indian Railways Institute of Electrical Engineering, Nasik Road)
ii. www.wr.railnet.gov.in/bctweb/ELECTRICAL.htm
iii. www.scrailway.gov.in
Study Material
Here you will get official GTU Syllabus, Question Bank, Old GTU exam papers, PPT’s and Lecture Notes.
Teaching Scheme
Lecture
Tutorial
Practical
Credit
Examination Scheme
Theory (ESE)
Theory (PA)
Practical (ESE)
Practical (PA)
Total Marks
Video Lectures
Blog
Advantage and Disadvantage of Electrical Drive
Theory Advantage of Electrical Drive: Flexibility Cleanliness Space saving Better operating characteristics Remote control Automatic Control Easy starting Reduced maintenance Disadvantage of Electrical Drive: Used only where the electric supply is available...
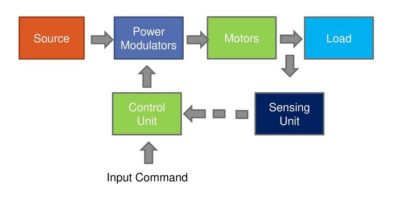
Block Diagram of Electrical Drive
Theory Drives: Any machine comprises of the three following components. Prime Mover Power Transmission system Machine Power is generated by the prime mover. The prime mover may be electric motor, steam engine, IC engine or a water turbine. Power generated by the prime...
Examples
Quiz
A Train is required to run between two stations 1.6 km apart at an average speed of 40 km/hr. The run is to be made to a simplified quadrilateral speed-time curve. If the max speed is to be limited to 64 kmph, acceleration to 2 kmphps, and coasting and braking retardation to 0.16 kmphps and 3.2 kmphps respectively. Determine the duration of acceleration, coasting, and braking periods.


0 Comments